Recently, Wang Jiahong and Yu Xuefeng of the Material Interface Research Center of the Institute of Materials Research, Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences have made new progress in the field of high-temperature nitrogen fixation at room temperature and pressure, and developed a black phosphorescent electrode with excellent photoelectric synergistic nitrogen fixation for ammonia synthesis. The related work was published in "Advanced Function Materials" (Advanced Function Materials, DOI: 10.1002 / adfm.202002731) under the title of "Photoelectrochemical Synthesis of Ammonia with Black Phosphorus" and was selected as the back cover of the magazine story. Associate researcher Wang Jiahong and researcher Yu Xuefeng are the corresponding authors of the article, and assistant researcher Liu Danni is the first author of the article.
Ammonia is an important chemical raw material in industrial and agricultural production and a new type of hydrogen-rich energy carrier. At present, ammonia synthesis is mainly carried out by the Haber-Bosch method under high temperature and high pressure (350-550 ° C, 150-350 atm), which consumes high energy and is accompanied by a large amount of greenhouse gas emissions. Therefore, the green and environmentally friendly ammonia synthesis technology using nitrogen and water as raw materials at room temperature and pressure has gained wide attention. The photoelectrochemical technology combining electrocatalysis and photocatalysis process provides a more efficient technical platform for ammonia synthesis at room temperature and pressure. As a two-dimensional direct bandgap semiconductor, black phosphorus has many advantages such as wide light response range, high carrier mobility, rich edge active sites, and weak hydrogen adsorption. potential.
In this study, the research team assembled high-quality black phosphorus microchips obtained by electrochemical intercalation stripping on a conductive substrate into a nitrogen-fixing photoelectrode through a new type of spin-coating-fast evaporation technology. In an acid electrolyte saturated with nitrogen, black phosphorus exhibits better electrocatalytic nitrogen fixation performance for ammonia synthesis (24.1 μg / h / mgcat, Faraday efficiency 5.5%). Under the synergetic effect of photoelectricity, the black phosphorescent electrode's ammonia production rate and Faraday efficiency have been greatly improved, reaching 102.4 μg / h / mgcat and 23.3%, respectively, which is the best record of the same type of non-metallic nitrogen fixing catalyst. In further research, the research team verified the source of nitrogen and eliminated the interference of impurities through quantitative isotope labeling; the photoelectrochemical Mott-Schottky spectroscopy study proved that the light excitation increased the flat band potential of the black phosphorescent electrode and promoted the electrochemistry of the electrode surface In addition, the cathode electric field and inert environment in the reaction system also contribute to the interface charge separation, which can effectively protect the black phosphorescent electrode from oxidation, so that it exhibits good stability in the process of photoelectric nitrogen fixation.
This research work revealed the excellent photoelectric nitrogen fixation performance and mechanism of black phosphorus, and expanded the application of black phosphorus in the field of heterogeneous catalysis; the effect of one plus one greater than two exhibited by photoelectric cooperative catalysis also provided the development of ammonia synthesis at room temperature and pressure New ideas. The research work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Youth Innovation Promotion Association of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, and the Frontier Science Key Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
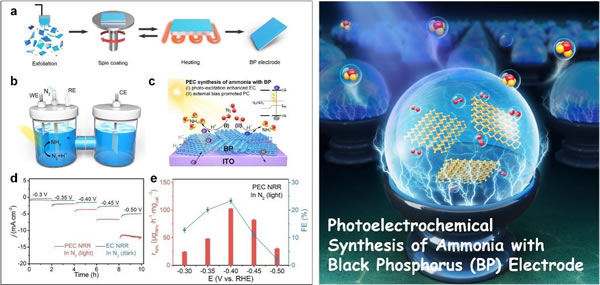
Left: (a) Schematic diagram of the preparation process of the black phosphorescent electrode, (b) Schematic diagram of the photoelectric nitrogen fixation device at normal temperature and pressure, (c) Schematic diagram of the photoelectric nitrogen fixation principle of the black phosphorescent electrode, (d) Electrocatalytic and photocatalytic current density maps at different potentials, (e) Data graph of black phosphorus photoelectric nitrogen fixation performance. Right: Schematic diagram of the nitrogen fixation process of the black phosphorescent electrode.
Dining Table Sets,Metal Dining Table Sets,Dining Table Set For Living Room, Dining Table With Chair Sets
FOSHAN CITY LESHUN RONGHUI FURNITURE CO.LTD , https://www.sdwinfurniture.com