In response to reports from international media, NASA faced a significant challenge after retiring its space shuttle fleet: it no longer had a manned spacecraft capable of reaching orbit. For transporting supplies to the International Space Station, Europe and Japan relied on their own cargo ships, while crew transportation was entirely handled by Russia. Each seat on a Russian spacecraft cost an eye-watering $62 million. To address this gap, NASA partnered with several private space companies, leveraging their cost-effective solutions to regain the capability of sending astronauts into low Earth orbit.
1. Private companies are set to play a larger role in NASA's future space programs.

2. The Falcon 9 rocket and Dragon spacecraft have been combined to form a reliable system for human spaceflight.
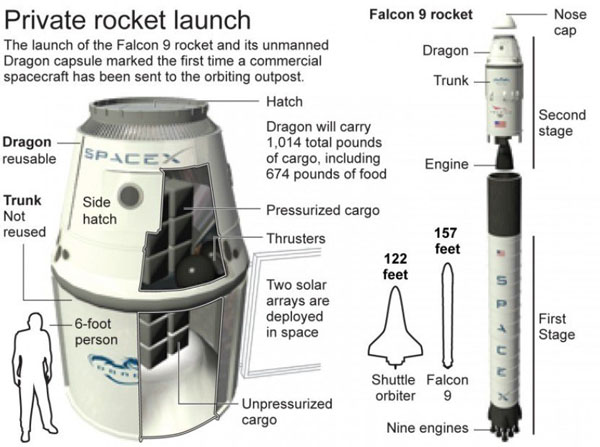
John Logsdon, a professor at George Washington University’s Institute for Space Policy, argues that private companies often outperform government agencies in terms of efficiency and cost control. One such company, based in California, specializes in orbital services like rockets and spacecraft, contributing significantly to NASA’s goals.
3. The "Dragon" spacecraft is designed for docking with the International Space Station.
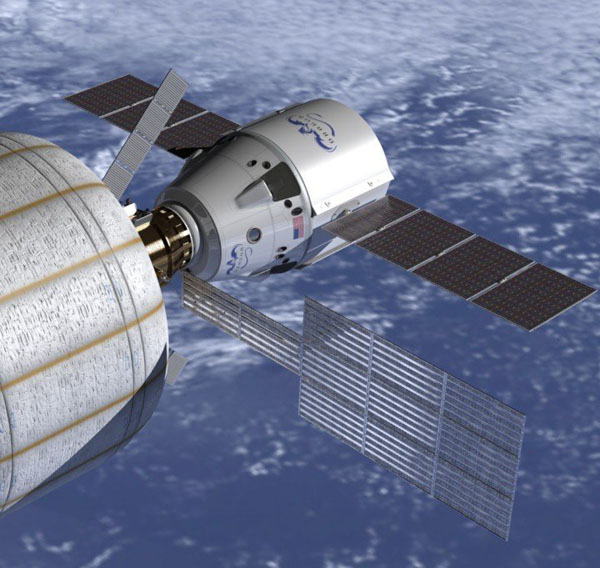

Elon Musk, CEO of SpaceX, signed a $1.6 billion contract with NASA to conduct at least 12 round-trip missions. Experts suggest that as private companies expand their presence in orbital launches, the reliance on Russian spacecraft will decrease. Initially, the "Dragon" spacecraft is aimed at carrying astronauts.
4. Boeing's CST-100 spacecraft is being developed as the next-generation vehicle for ISS transport.
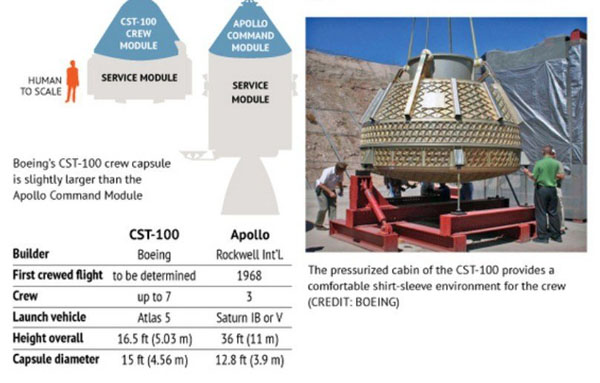
Boeing, along with Sierra Nevada Corporation, has also introduced its own suborbital vehicles. The CST-100 is seen as a key player in future crewed missions to the ISS.
5. Sierra Nevada's Dream Chaser suborbital spacecraft.

The Dream Chaser, resembling the space shuttle, is launched using Hercules rockets. Its advanced aerodynamic design makes it a promising candidate for future space missions.
6. Bigelow Aerospace's inflatable space station.
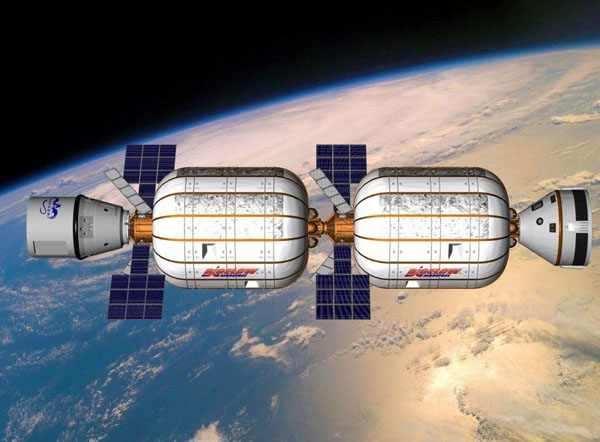
Beyond suborbital vehicles, some private companies are exploring space station concepts. Bigelow Aerospace has deployed an inflatable module that could serve as a future lunar base, supporting up to six astronauts in life and work. This innovation marks a new era in space exploration, driven by both public and private efforts.
Mechanical Anchor Bolt
Hebei Qianmu Fastener Manufacturing Co., Ltd , https://www.qmjgjfasteners.com